It also has metal electrodes that supply the current with sources external to. The entire thing is put in the form of a frame that has a window to transmit light in the form of light. A light beam of the correct wavelength leads to the creation of electron-hole pair holes. This increased number of holes and electrons increases its conductivity in the semiconductor which causes a decrease in the photoresistor's resistance.
A photoresistor is referred to as an element of semiconductor that is junction-free that, under the effect of light radiation alters its resistance. The active (photosensitive) component of a photoresistor is thin layer of semiconductor deposited on an electro-conductive substrate. It also has metal electrodes that supply the current with sources external to. The entire thing is put in the form of a frame that has a window to transmit light in the form of light. A light beam of the correct wavelength leads to the creation of electron-hole pair holes. This increased number of holes and electrons increases its conductivity in the semiconductor which causes a decrease in the photoresistor's resistance.
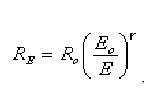
Where Ro is the resistance of the photoresistor at the intensity Eo (usually 10 lx), while r is a constant coefficient, the size of which depends mainly on the type of semiconductor material (for example, for CdS r = 0.5 - 1).
In the application of photoresistors as radiation detectors these technical specifications are primary significance:
T - temperature of the detector by detector temperature, it refers to the temperature of the active zone, which is for photoresistors it is the temperature the semiconductor layer which is subject to light is at when the detector is operating.
The area of the active area of detector A in cases of photoresistors we can make an approximatement that it's an approximate size for the surface of the semiconductor which is illuminated. In this topic it would be good to know how does a photodiode work to deeply know the topic.
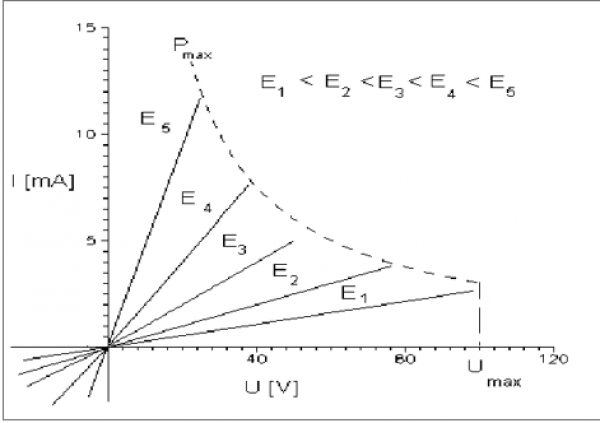
Electrical parameters that relate with the operation point of the photoresistor. the permissible voltage between both ends of the photoresistor's Umax, the permissible electrical power dissipated from the photoresistor Pmax, the resistance's dark voltage when it is operating at a certain voltage at its terminals , and the voltage that determines its operating points.
Sensitivity of the detector S every detector has an operating area in which the amount that the output signal produces is proportional to that input signal. In this range, the ratio between these two values is referred to as"sensitivity" of the detector. In the case of radiation detectors, either current sensitiveness or voltage sensitivity is defined. The term "current sensitivity" refers to the proportion of the increase of the photoelectric short-circuit current to the radiation flux that is incident at the detection. Voltage sensitivity is proportional to the increases of the photoelectric voltage that occur at the resistance of the load (when that it is properly matched) to the flux of radiation that is reflected on the detector. The units used to measure sensitivity for radioactive detectors is amps for watt or volts / Watt, or.
The detector time constant is the duration of the signal rise; the duration required to achieve 1-e-1 of the highest sign-up value (about 63 percent).
Time constant of decay of signal is the amount of time needed for a signal's decay to e-1 of its highest value (about 37 percent ).
In the description abbreviated of a photoresistor in place of RE(E) character, we will use it is the numbers of the darkness resistance (i.e. the amount of resistance that the photoresistor experiences when its visible surface has been completely black) in addition to the light resistance RE when there is a particular magnitude of light intensity E (most typically E=1000 lx) are typically listed. Other important particular parameters of photoresistor models include highest permissible voltage Umax as well as the maximum power dissipated through this element, and the temperature sensitivity coefficient that is average as.